If you’ve ever wondered why running a Bitcoin node requires beefy hardware, you’re not alone. The challenge boils down to something called the UTXO set, essentially Bitcoin’s address book...
by Daniel Molina & Jordi Herrera-Joancomartí — November 2025 The challenge of decentralization security When Ethereum transitioned from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake (PoS), it didn’t just...
When we talk about self-custody and protecting our bitcoins, we understand that the seed used to generate our private keys must be completely isolated and stored securely. The best-known...
Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies in general use cryptography to ensure the ownership of coins, among many other aspects. The security is based on “hard” problems that guarantee the basic properties,...
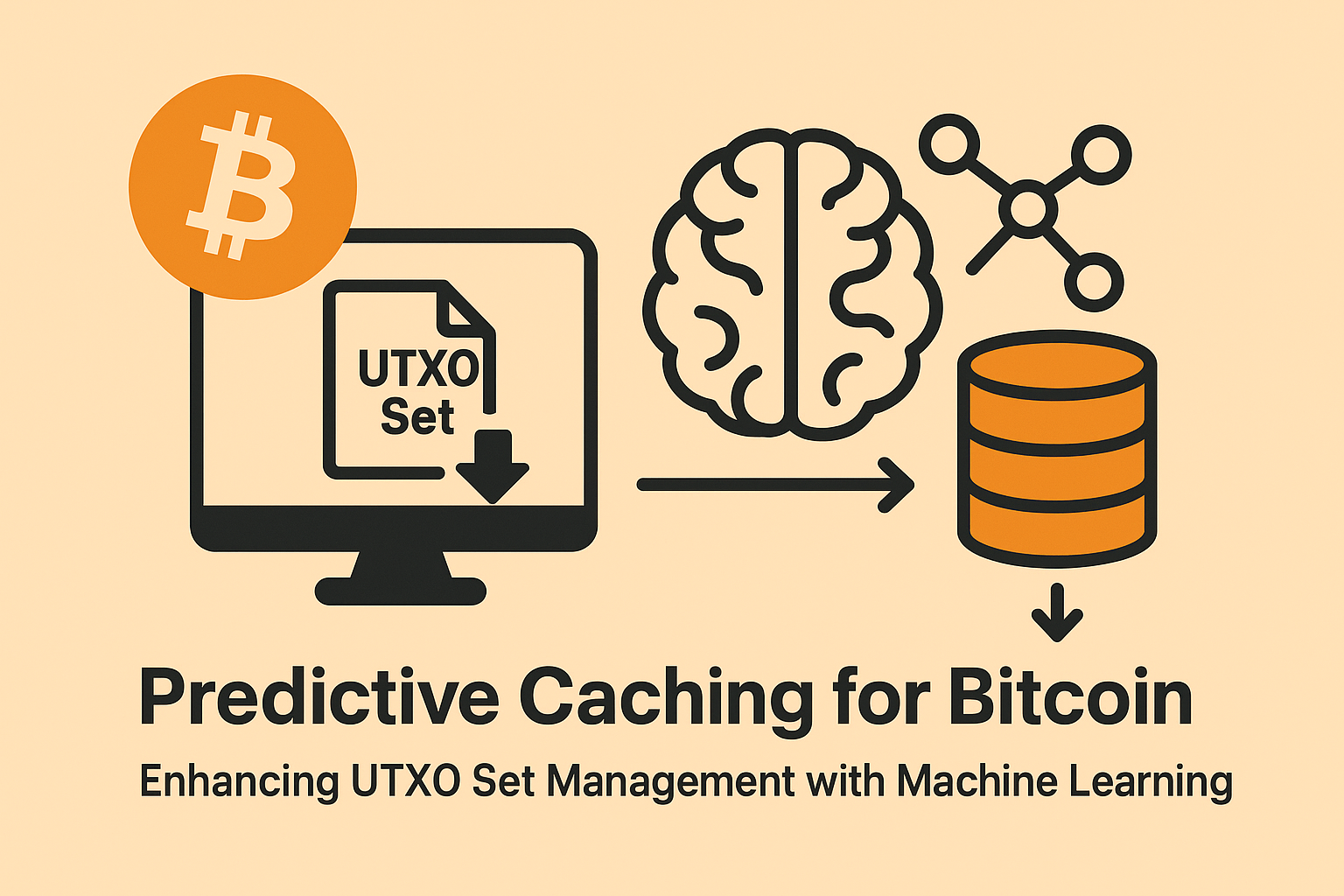
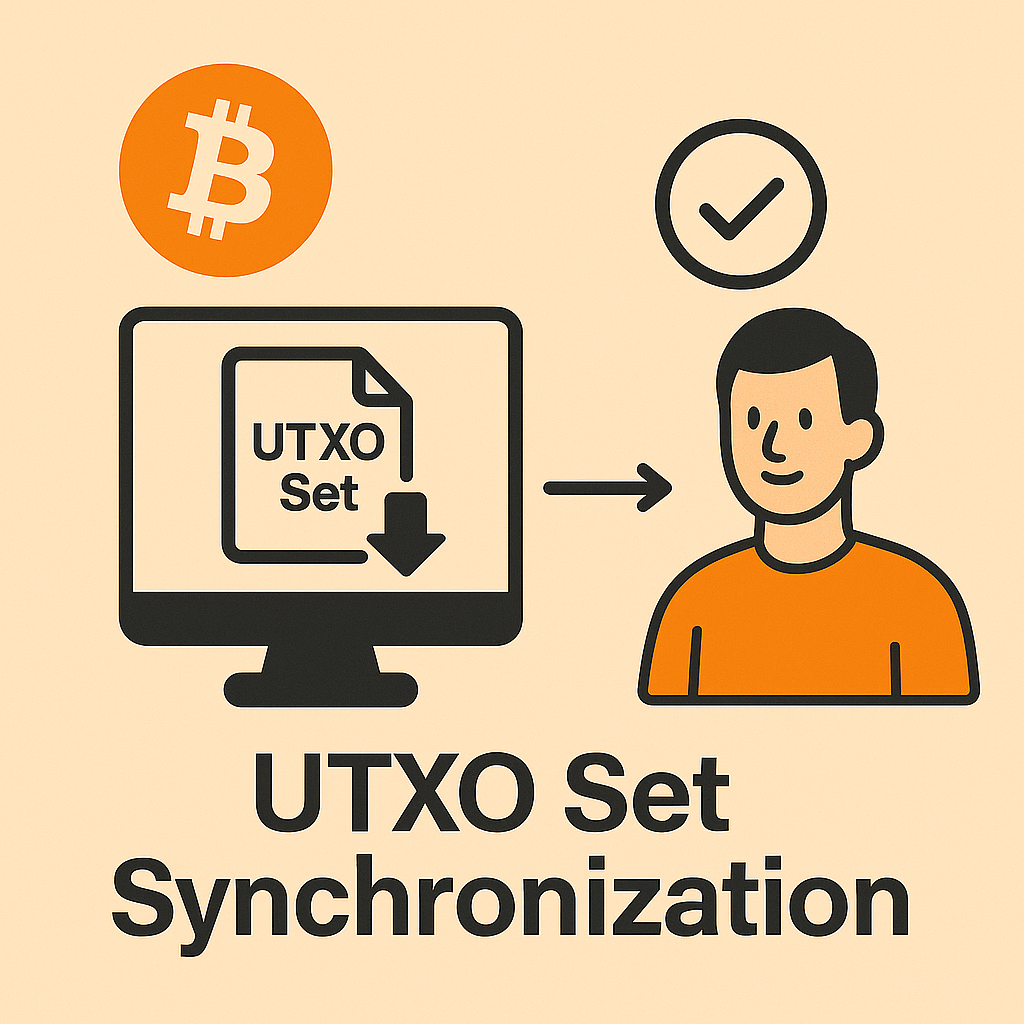
Accelerating Bitcoin Initial Sync with the UTXO Set We’ve all experienced situations where our Bitcoin node stops working—maybe the Raspberry Pi crashes, the disk fails, or we simply need...
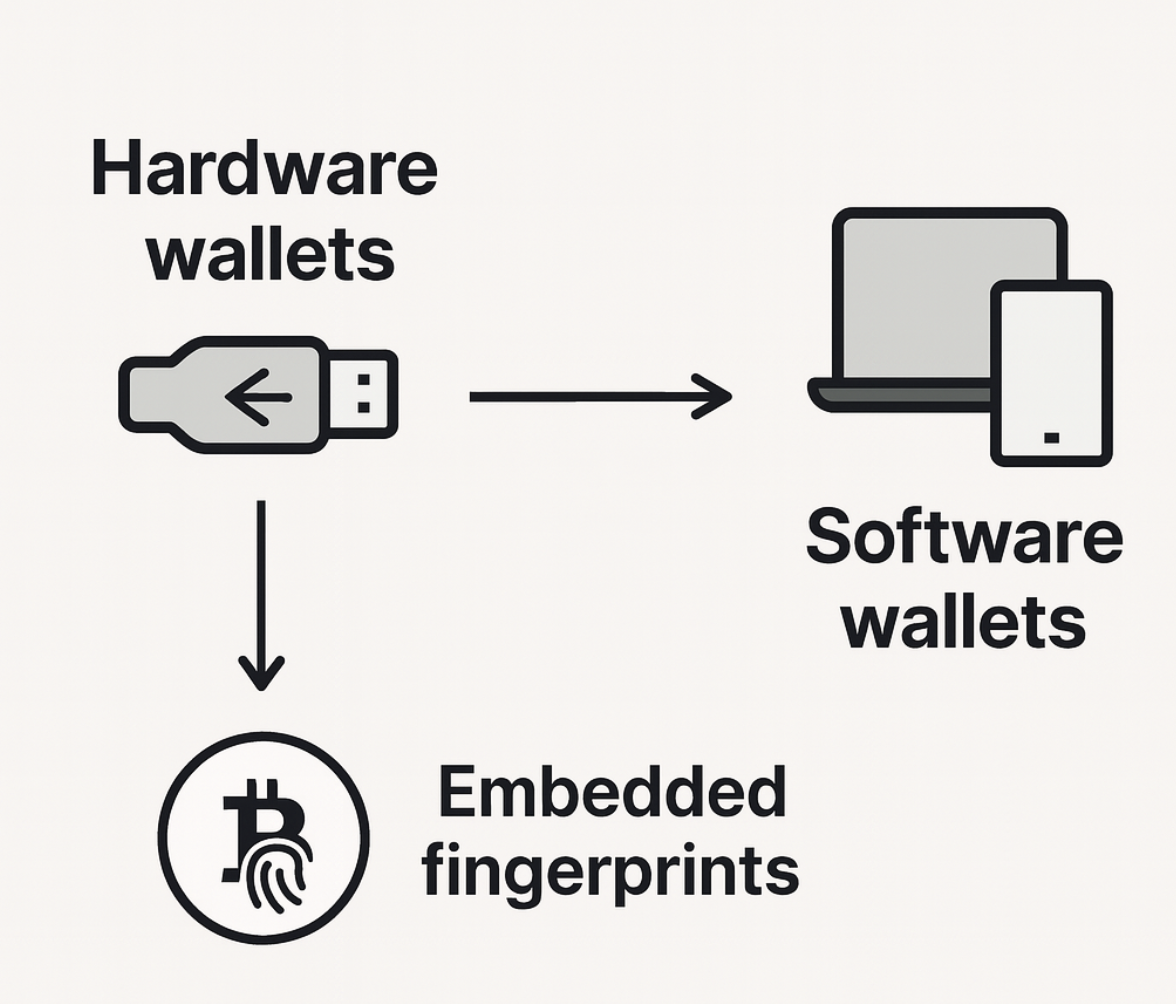
We are currently carrying out an in-depth study on wallet fingerprinting in Bitcoin, aiming to understand how different wallets — both software and hardware — shape transactions and what...
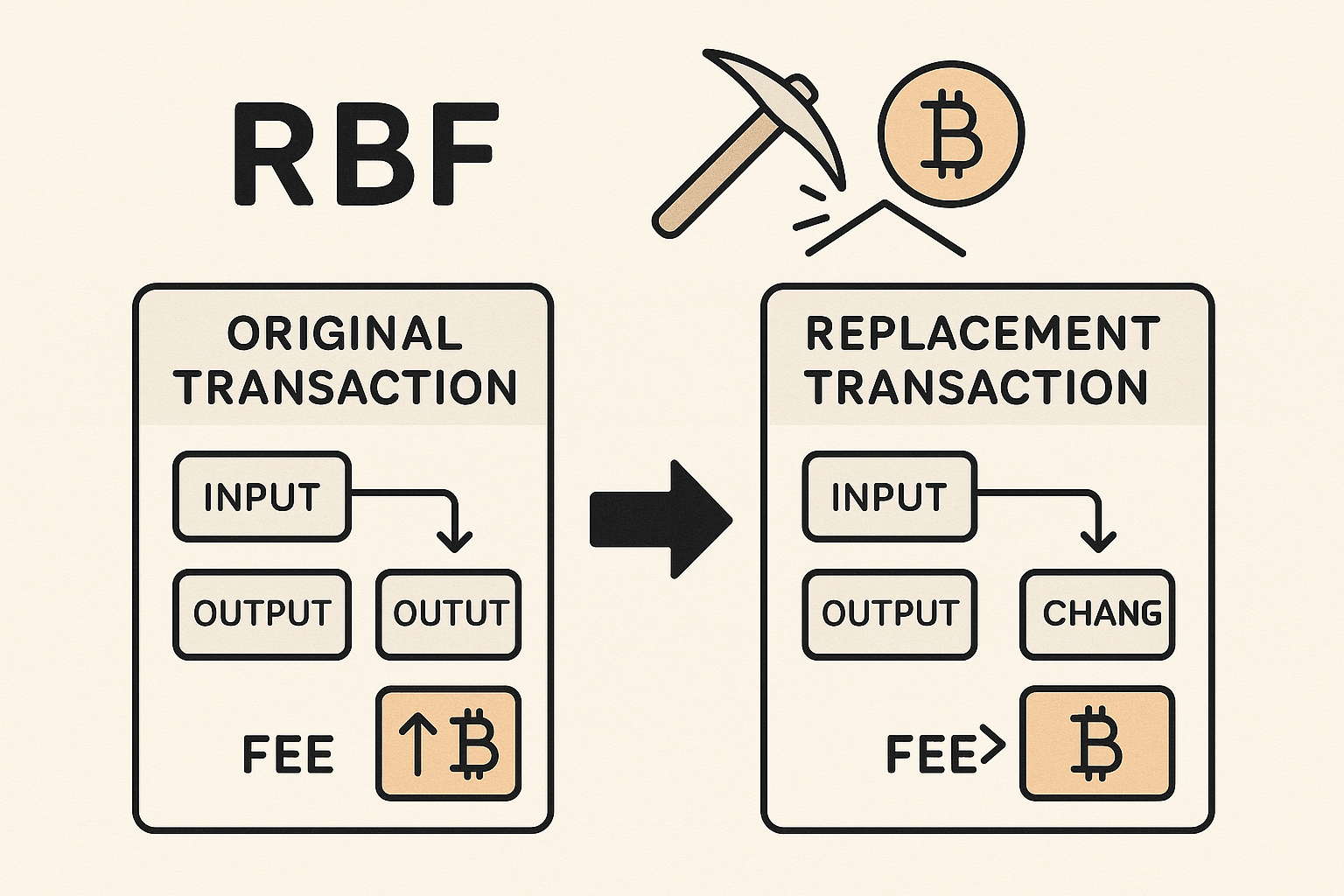
Transaction fees play a fundamental role in the proper functioning of the Bitcoin protocol. These fees act as an economic incentive for miners, who compete to create a block...
Introduction Detecting malicious activity in cryptocurrency networks like Bitcoin relies on datasets labeled with licit and illicit transactions. However, these datasets often suffer from class imbalance: the number of...
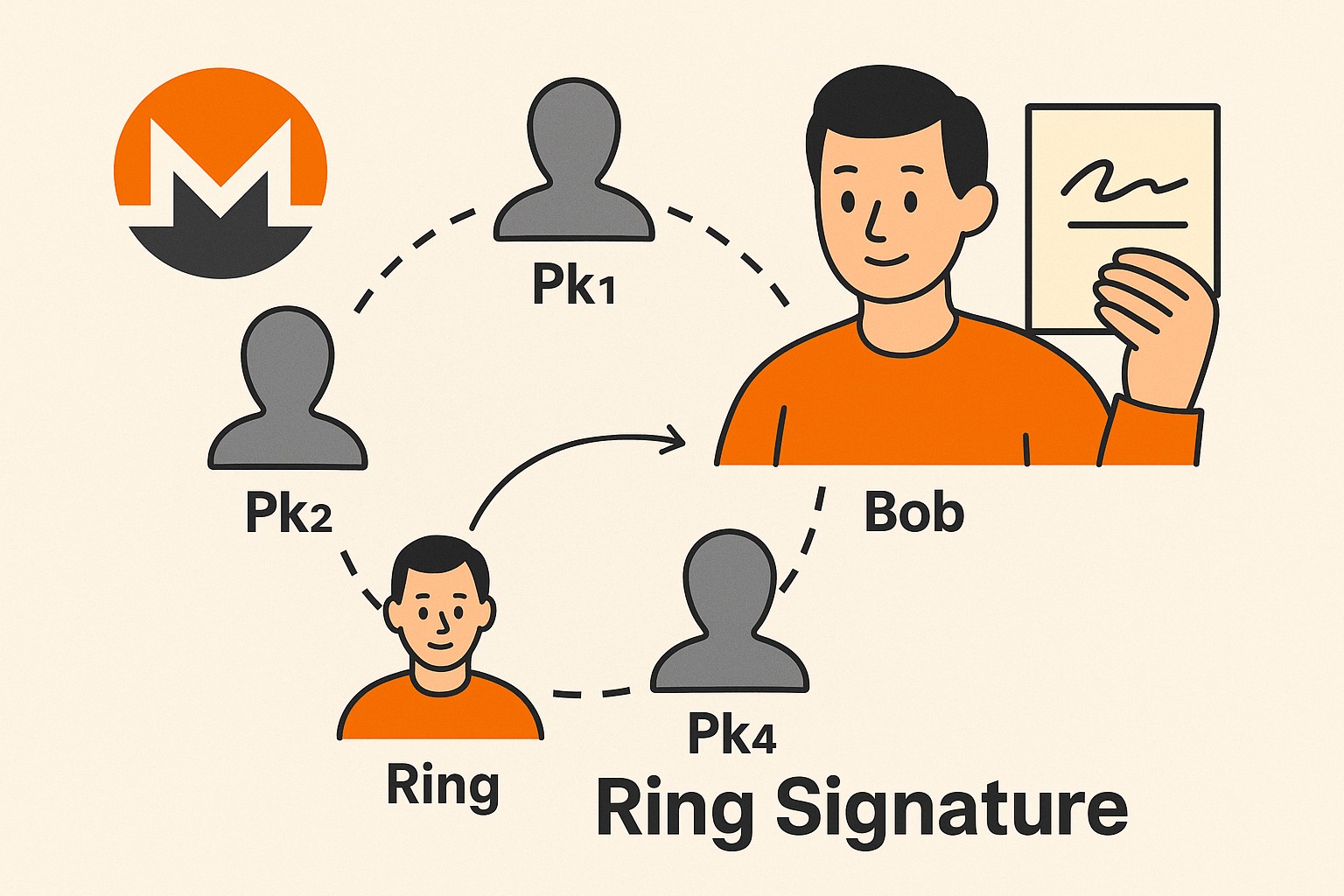
Introduction Ring Signatures Overview The main idea behind ring signatures is that a user $u$, who is part of a user group $$R = {\,u_1,\,u_2,\,\dots,\,u_i},$$ can sign a message...
During my initial research period at UAB, I began developing a replica of the real Bitcoin mainnet. While this might sound unusual—especially given the existence of testnet and regtest...